AIR RESTISTANCE
The force resulting from air creating friction on an object, magnitude dependent on surface area
ALTIMETER
A device that can measure its height from a zero ground position
APOGEE
The peak altitude of a model rocket
ASSEMBLY
A set of parts put together in a purposeful way or according to design
BODY TUBE
The portion of a rocket that houses most of the parts
CENTER OF GRAVITY
The point on an object where the weight on either side is balanced with the other
CENTER OF PRESSURE
The point on an object where the air flow from all directions is balanced
DRAG
The force that opposes motion due to various factors including air resistance
ENGINE (MODEL ROCKET)
A miniature non-metallic solid fuel rocket motor that contains propellant and may contain a delay element and an ejection charge. Designed to impart force to accelerate the rocket during flight and to activate the recovery system at or near maximum altitude.
FINS
Passive stabilizing and guiding unit of a model rocket; an aerodynamic surface projecting from the rocket body for the purpose of giving the rocket direction and stability.
FORCE
A push/pull on an object resulting from interaction with another object, either with or without contact.
LAUNCH LUG
A round, hollow tube that slips over the launch rod to guide the model during the first few feet of flight until sufficient airspeed is reached to allow the fins to function.
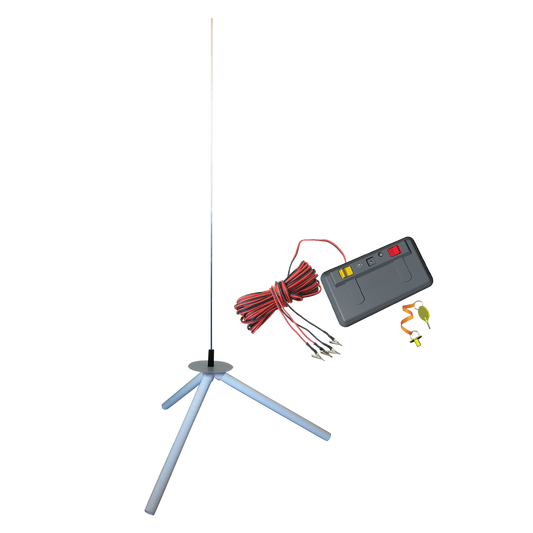
LAUNCH SYSTEM
Stable launching rod, remote starter system, and other components needed to launch a model rocket.
NOSE CONE
The forwardmost part of the rocket.
RECOVERY SYSTEM
A device incorporated into a model rocket for the purpose of returning it to the ground in a safe manner. Usually achieved by creating drag or lift to oppose the acceleration of gravity. All model rockets must employ a recovery system, such as a parachute.
RECOVERY WADDING
Non-flammable paper that protects the recovery system from melting the parachute when the ejection charge occurs.
STABILITY
An object or system that is in the state of minimal unbalanced forces
VELOCITY
The speed of an object in a specified direction